DDA Raycasting and Block Interaction
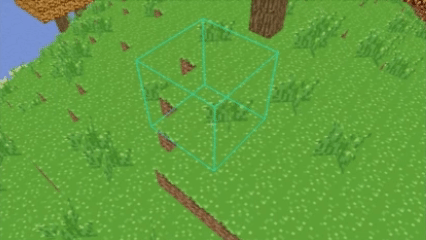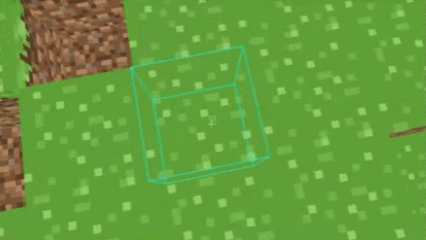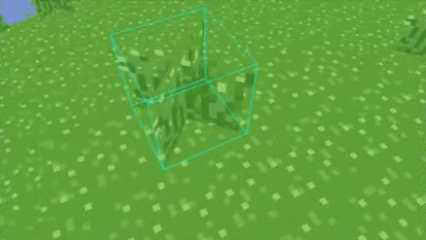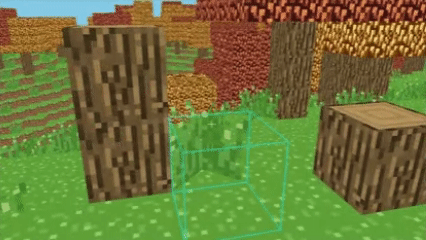
Digital Differential Analysis (DDA) raycasting is an algorithm used to trace a ray through a grid-based system, either in a 2D or 3D space like my voxel world.
It determines which voxel a ray intersects by stepping through one voxel at a time along the ray's direction.
In my voxel engine, DDA is used to
- detect which block the player is hovering/pointing at.
- place and break a block
If you want a visualized explanation of DDA, check out this video.
How DDA Raycasting Works
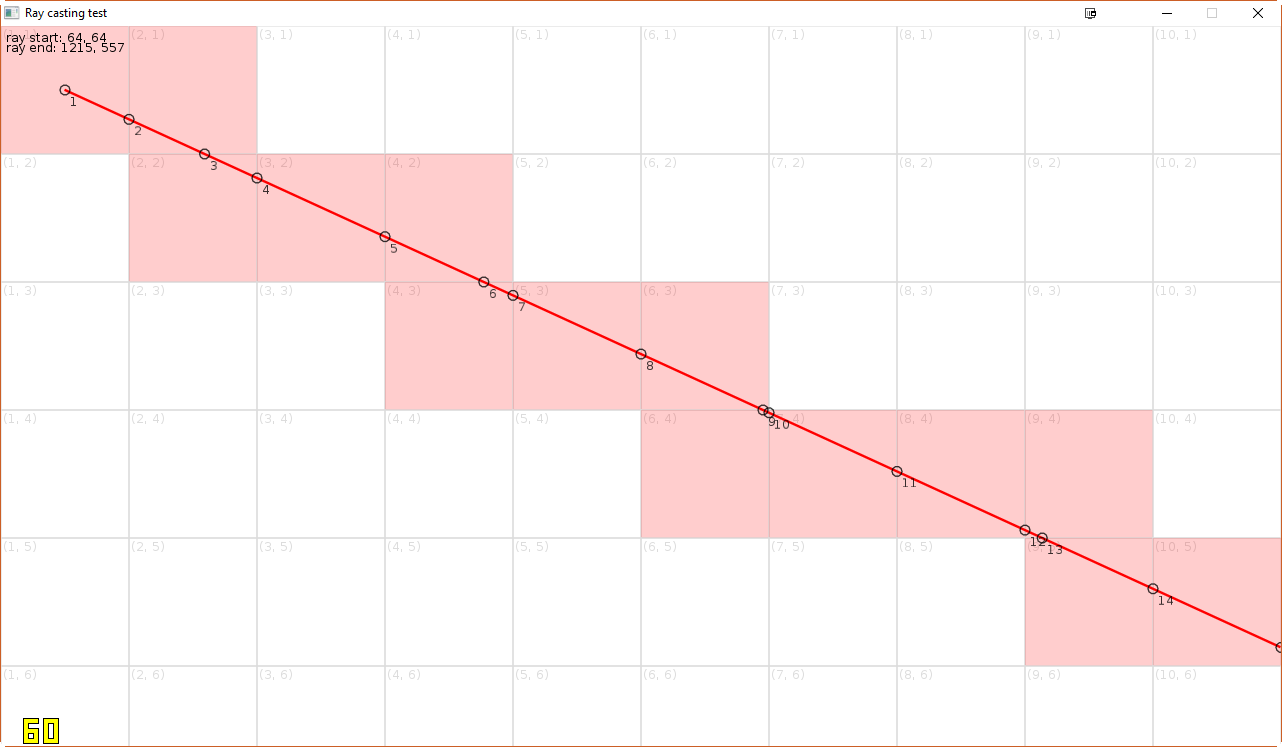 The ray starts from the camera's position and increments along te x, y, and z axes depending on which axis the ray will cross next.
This continues until the ray hits a block or reaches its maximum legth.
The ray starts from the camera's position and increments along te x, y, and z axes depending on which axis the ray will cross next.
This continues until the ray hits a block or reaches its maximum legth.
To access the voxel the ray intersects, the ray's current world-space coordiate is converted into:
- chunk-space coordinate to identify which chunk the voxel belongs to.
- voxel-space coordinate to access the specific voxel within that chunk. This is an index of the blocks' array.
Coordinate Conversion
World to chunk-space coordinate:
ivec3 world_to_chunk_coord(vec3 world_coord) {
return {
floor(world_coord.x / chunk_size),
floor(world_coord.y / chunk_size),
floor(world_coord.z / chunk_size)
};
}
World to voxel(local)-space coordinate:
ivec3 world_to_local_coord(vec3 world_coord) {
ivec2 chunk_origin = world_to_chuk_coord(world_coord);
ivec3 local_coord = {
floor(world_coord.x - chunk_origin.x * chunk_size) + 1,
floor(world_coord.y - chunk_origin.y * chunk_size) + 1,
floor(world_coord.z - chunk_origin.z * chunk_size) + 1
};
return local_coord;
}
floor() ensures we map the world coordinate to the voxel beneath or at that point. (i.e. With a coordinate (-1.1, 0.5, 2.7), we want to access the voxel at (-1, 0, 2)). This is for consistent block targeting.
The + 1 offset accounts for the extended block array size to ensure only owned voxels are accessed, not the ones at boundary. The boundary layer is for storing the information of blocks at adjacent chunks and using it for chunk meshing.
With a given local coordinate, a voxel can be accessed like this:
chunk.blocks_array[local_coord.x][local_coord.y][local_coord.z];
Block Placing and Breaking
Once DDA raycating works, block interaction is easy to implement. You only need to change the block texture.
- placing a block: set the block type to targeted type
- breaking a block: set the block type to Air
- re-build and render the chunk mesh.
- additionally add sound effects differently based on block type.
DDA Raycasting Implementation in 3D Voxel World
void Camera::raycast() {
vec3 origin = position; //camera position
vec3 dir = direction; //camera direction
vec3 delta = { //unit step size in x, z, and y axis
abs(1.0f / dir.x),
abs(1.0f / dir.y),
abs(1.0f / dir.z),
};
vec3 ray_length, step;
vec3 current = floor(origin);
if (dir.x < 0) {
step.x = -1;
ray_length.x = (origin.x - current.x) * delta.x;
}
else {
step.x = 1;
ray_length.x = (current.x + 1 - origin.x) * delta.x;
}
if (dir.y < 0) {
step.y = -1;
ray_length.y = (origin.y - current.y) * delta.y;
}
else {
step.y = 1;
ray_length.y = (current.y + 1 - origin.y) * delta.y;
}
if (dir.z < 0) {
step.z = -1;
ray_length.z = (origin.z - current.z) * delta.z;
}
else {
step.z = 1;
ray_length.z = (current.z + 1 - origin.z) * delta.z;
}
float dist = 0.0f;
while (dist < max_ray_length) {
Block* block = cm.get_block_worldspace(current);
if (block != nullptr) {
hovered_block = block;
if (block->type != none) {
return;
}
}
//increment in the direction where ray_length is shorter
if (ray_length.x < ray_length.y) {
if (ray_length.x < ray_length.z) {
//horizontal step in x-axis
current.x += step.x;
dist = ray_length.x;
ray_length.x += delta.x;
}
else {
//horizontal step in z-axis
current.z += step.z;
dist = ray_length.z;
ray_length.z += delta.z;
}
}
else {
if (ray_length.z < ray_length.y) {
//horizontal step in z-axis
current.z += step.z;
dist = ray_length.z;
ray_length.z += delta.z;
}
else {
//vertical step in y-axis
current.y += step.y;
dist = ray_length.y;
ray_length.y += delta.y;
}
}
}
}